What is CAD Software?
The List: Top 10 From Beginner to Professional Level
1. TinkerCAD
– Free
2. FreeCAD
FreeCAD is a completely free parametric 3D modeling tool that is open-source and enables you to design real-life objects of any size. The parametric component makes editing easier. You can go to your model’s history and change the parameters to get a different model. This software is not designed for professional purposes but is a good training tool. The options it offers are quite basic but a good starting point when you have no experience.
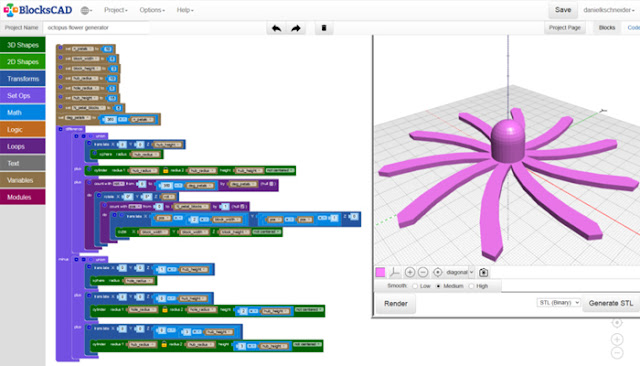
3. BlocksCAD
This 3D software is specifically created for educational purposes, its development is done so that anyone can later use OpenSCAD, a more professional CAD software. The commands for the development of the objects and their transformations are represented by colour blocks, reminiscent of the well-known construction toys, LEGO. BlocksCAD’s code is fully compatible with OpenSCAD’s so you can give your models the last touch up on there. Export formats can be OpenSCAD or STL. To make sure that anyone can learn to use the software, BlocksCAD has a Youtube channel with different tutorials on 3D modeling.
– Beginner Level
– Free
4. Creo
Creo CAD software is one of the market leaders in product design, developed by Parametric Technology Corporation more than 30 years ago. It integrates many functionalities such as thermal, structural, motion, parametric and freestyle surface generation and direct modeling. It is a complete tool, ideal for additive manufacturing, that will allow you to perform all your dimensioning calculations while modelling your final idea. The latest Creo 5.0 version was released in 2018 and features an improved user interface, redesigned for a better handling. A 30-day trial version is available free of charge.
5. Fusion 360°
Fusion 360 is a cloud-based 3D CAD program. It’s unique in the sense that it uses the power of the could to bring together design teams to collaborate on complex projects. An advantage of the Fusion 360° platform is it stores the entire history of the model including all the changes. It contains numerous design options, including freeform, solid and mesh modeling. It operates on a monthly payment subscription basis. The developers also regularly update the features, making it better as new instalments come along. It runs on multiple platforms and allows users to access their information wherever they want. In i.materialise’s poll in 2017, they noticed a jump in the program’s popularity in the last two years. Many people have praised the software’s professional capabilities and user-friendly interface and workflow.
– Intermediate Level
– Payment: $60/month or $495/year
– Free for students, educators & academic institutions
6. Solidworks
Published by Dassault Systèmes, it is often used by professional 3D designers. It is a parametric featured-based model. The software includes a wide range of features such as design validation tools, or reverse engineering. It tends to be used for industrial objects. It is quite practical and detailed. One of its special features is that unlike many other software that mimic curves through gently inclining flat structures, Solidworks uses a system of NURBS. This system allows to create very detailed curvatures. Also, instead of polygonal modeling, it uses dimensional sketching so that resizing becomes far less of a hassle. One disadvantage that is often brought up by users of the software is the limited ability to import .STL files. If you wish to download and edit .STL files, a secondary program will most likely be necessary. The file format is very much an output file format and not intended for post-design processing.
– Professional Level
– One license is $3,995
7. AutoCAD
AutoCAD software from Autodesk was one of the first CAD software to be released on the market in 1982, making it a very established CAD software across industries. Even though AutoCAD is popular and widely used, in the 3D printing community its popularity has decreased lately according to i.materialise’s poll. Many users cite that although it is ideal for 2D drafting, it is not the easiest to use for 3D modeling. Indeed, the learning curve to master macros and scripts is steep for moving beyond simple parts. The software is aimed at professionals with experience in programming models algorithmically. If you have that skill, there is little you can’t do with AutoCAD. The 3D models can readily be converted to STL files for 3D printing. Since 2010, AutoCAD was released on a mobile and web-app as well, called AutoCAD 360.
– Professional Level
– From $185/month or $1,470/year
– Free and fully functional version to download for students and faculties.
8. CATIA
The CATIA CAD solution has historically been developed for Dassault Aviation’s own needs. It is more than a simple CAD Software, as it is also a multi-platform software suite for CAD, CAM (Computer Aided Manufacturing), CAE (Computer Aided Engineering) and more. It is powered by Dassault Systèmes’ 3DEXPERIENCE platform. CATIA innovates product design and experience by integrating various approaches in product design and development, enabling multiple disciplines to leverage their existing tools throughout the stages of product development process. Therefore, the software is very useful for industrial and creative designers, mechanical engineers, and systems architects. CATIA provides a 3D design environment that enables online people and stakeholders to share product designs and collaborate on product modelinmodelingg
– Professional Level
– Starting price around $10,000
9. OpenSCAD
OpenSCAD is a free, open-source CAD software aimed at making solid 3D models. It is suitable for experienced users seeking a platform for an elaborated project. Also, given its Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG) and the Extrusion of 2D outlines, this software is intuitive for coders/programmers. It is great for simple shapes that are already parametrically defined. Since it is completely based on description language, the program will not be intuitive for everyone at all.
– Professional Level
– Free
10. Rhino
The company behind this software markets it as the world’s most versatile 3D-modeler. It is a commercial 3D computer graphics and CAD software. The program uses a precise and mathematical model known as NURB which allows to manipulate points, curves, meshes, surfaces, solids and more in all sorts of ways. Rhino3D’s strong point is its wide range of design features. It offers great versatility in creating complex 3D models. Many users have reported however that the software is difficult to learn and will take a lot of practice to master. It is also reportedly not the most accurate software at capturing user intent. The software is available for download in a variety of bundles on their website at various prices.





















